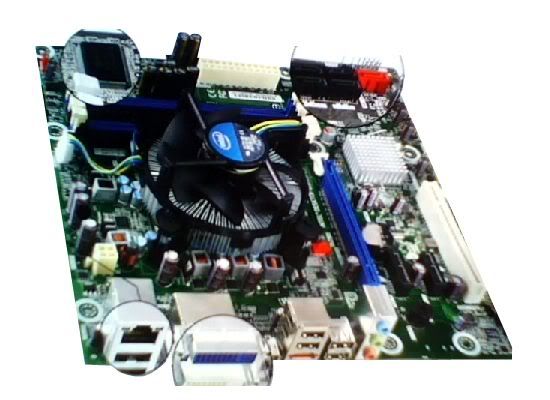
AMD Fusion APU.
The balance between performance X86, Graphics, and Parallel Computing.
AMD Fusion Accelerated Processing Unit (APU) is a category of AMD's latest mobile chips that had been carried Neo AMD Athlon processor, VIA Nano, Intel Atom, and Intel Core ULV.
AMD has long stated its intention to merge the ability of the x86 CPU (general purpose, and serial data processing) and discrete graphics GPU, which excel at data parallel processing. Precisely since they do a merger with graphics manufacturer ATI in 2006. finally in 2011 in Events CES 2011 in Las Vegas last January, AMD formally announced the official attendance at APU that claim is supported by a number of large vendors such as Acer, Asus, Dell, Fufitsu, HP, Lenovo, MSI, Samsung, Sony, and Thosiba.
APU is part of AMD's Fusion architecture introduced since 2009. combination of CPU and GPU in one chip APU that looks simple, but in fact, it is a series of development process and production process are complex and time consuming. Barriers are not just about hardware implementation in this case is to merge CPU and GPU, but also in the design process to work optimally on CPUGPU technology (general purpose computation of Graphics Processing Unit). Just like OpenCL and computers are starting to be used directly in the software, Fusion Architecture needs to be designed carefully to ensure that can be developed further for the next two or three generations. Other factors are the focus of AMD is to create compatible architecture with the previous generation architecture and next generation.
Unlike Intel which is independent in the chip manufacturing process.. AMD relies on other parties in the APU chip manufacturing process, for zacate APU (E series) and Ontario (Series C) using 40nm production technology from TSMC.and scheduled to finish in 2011, many others APU Fusion, such as the Liano (series A) are targeted for deskop, will use the 32nm production technology from Global Foundries. AMD Fusion APU first released, consisting of four series, two Serie (Zacate) and two series C (Ontario). Series E (zacate) targeted for mainstream notebook, all in one. And Small Form Factor (SFF) deskop, consisting of E (1.5GHz single core with a TDP of 18 W) and E-350 (dual core 1.6 GHz with TDP18W). The second series (Ontario) is targeted for a netbook or a tablet, consisting of C-30 (single core GHz with a TDP of 9 W 1.2) (1.0 GHz dual-core processors with TDP 9 W) C and-50.
Next target: consumer electronics
Intel has stated its intention to enter the consumer electronics area with the presence of atoms embedded chip, which is implanted in the Google TV. Although AMD has not entered into the world of tablet that becomes a trend in the market, AMD still believe if they X86 technology, is ready to compete with Intel and other development company.
AMD Fusion Accelerated Processing Unit (APU) is a category of AMD's latest mobile chips that had been carried Neo AMD Athlon processor, VIA Nano, Intel Atom, and Intel Core ULV.
AMD has long stated its intention to merge the ability of the x86 CPU (general purpose, and serial data processing) and discrete graphics GPU, which excel at data parallel processing. Precisely since they do a merger with graphics manufacturer ATI in 2006. finally in 2011 in Events CES 2011 in Las Vegas last January, AMD formally announced the official attendance at APU that claim is supported by a number of large vendors such as Acer, Asus, Dell, Fufitsu, HP, Lenovo, MSI, Samsung, Sony, and Thosiba.
APU is part of AMD's Fusion architecture introduced since 2009. combination of CPU and GPU in one chip APU that looks simple, but in fact, it is a series of development process and production process are complex and time consuming. Barriers are not just about hardware implementation in this case is to merge CPU and GPU, but also in the design process to work optimally on CPUGPU technology (general purpose computation of Graphics Processing Unit). Just like OpenCL and computers are starting to be used directly in the software, Fusion Architecture needs to be designed carefully to ensure that can be developed further for the next two or three generations. Other factors are the focus of AMD is to create compatible architecture with the previous generation architecture and next generation.
Unlike Intel which is independent in the chip manufacturing process.. AMD relies on other parties in the APU chip manufacturing process, for zacate APU (E series) and Ontario (Series C) using 40nm production technology from TSMC.and scheduled to finish in 2011, many others APU Fusion, such as the Liano (series A) are targeted for deskop, will use the 32nm production technology from Global Foundries. AMD Fusion APU first released, consisting of four series, two Serie (Zacate) and two series C (Ontario). Series E (zacate) targeted for mainstream notebook, all in one. And Small Form Factor (SFF) deskop, consisting of E (1.5GHz single core with a TDP of 18 W) and E-350 (dual core 1.6 GHz with TDP18W). The second series (Ontario) is targeted for a netbook or a tablet, consisting of C-30 (single core GHz with a TDP of 9 W 1.2) (1.0 GHz dual-core processors with TDP 9 W) C and-50.
Next target: consumer electronics
Intel has stated its intention to enter the consumer electronics area with the presence of atoms embedded chip, which is implanted in the Google TV. Although AMD has not entered into the world of tablet that becomes a trend in the market, AMD still believe if they X86 technology, is ready to compete with Intel and other development company.